BECE 2011 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. An example of a noble gas is
Solution: Noble gases are inert elements in Group 18 of the periodic table. Neon is a noble gas, while chlorine, nitrogen, and oxygen are not.
2. The structure that stores sperms temporarily in the male reproductive system of humans is
Solution: The epididymis is a coiled tube where sperm are stored and mature before ejaculation. The testes produce sperm, the sperm duct transports it, and the scrotal sac houses the testes.
3. Which of the following properties of alcohol as a thermometric liquid is correct?
Solution: Alcohol has a very low freezing point (around (-114^\circ \text{C}) for ethanol), making it suitable for thermometers in cold conditions. It is transparent, wets glass, and does not have a high freezing point.
4. In which of the following vegetation zones of Ghana does millet and sorghum grow well?
Solution: Millet and sorghum are drought-resistant crops that thrive in the Guinea savannah, characterized by lower rainfall and a longer dry season compared to forest or transition zones.
5. Which of the following methods is/are used for preserving fish?
I. Canning
II. Frying
III. Smoking
Solution: Canning, frying, and smoking are all methods used to preserve fish by preventing microbial growth and extending shelf life.
6. Which of the following practices in the home can prevent disease infection?
Solution: Covering food prevents contamination by microbes or insects, reducing the risk of disease. The other options promote infection.
7. An example of a semimetal is
Solution: Silicon is a semimetal (metalloid) with properties between metals and nonmetals. Calcium, lithium, and sodium are metals.
8. Which kind of energy transformation takes place in an electric motor?
Solution: An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy to produce motion.
9. Landrace is a breed of
Solution: Landrace is a breed of pigs known for its adaptability and meat production qualities.
10. In flowering plants, the stamen is made up of
Solution: The stamen, the male reproductive part of a flower, consists of the anther (produces pollen) and filament (supports the anther).
11. Which of the following statements about a transistor is correct?
Solution: Transistors amplify or switch electrical signals. They have three leads (emitter, base, collector) and two junctions, not three, and are not equivalent to diodes.
12. An atom has 6 protons and 7 neutrons in its nucleus. What is its mass number?
Solution: The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons. Here, (6 + 7 = 13).
13. A record of daily activities on a farm is termed
Solution: A farm diary records daily activities, such as tasks performed and observations, unlike specific records for labor, inventory, or production.
14. Which of the following devices work(s) on the principle of transmission of pressure in fluids?
Solution: All three devices use hydraulic principles, relying on the transmission of pressure through fluids to function.
15. Which of the following crops is not correctly matched with its group?
Solution: Cowpea is a legume, not a cereal crop. Cocoa is a beverage crop, coconut is an oil crop, and cocoyam is a tuber crop.
16. Which of the following substances is a salt?
Solution: A salt is formed from the reaction of an acid and a base. (\ce{CaCl2}) is a salt, while (\ce{H2SO4}) and (\ce{HCl}) are acids, and (\ce{NaOH}) is a base.
17. In which part of the digestive system of a fowl does grinding of feed take place?
Solution: The gizzard, a muscular organ, grinds food in a fowl’s digestive system, often with the aid of grit.
18. The parts of a bony fish that are used to control the level at which the fish swims are known as
Solution: Pectoral and pelvic fins help bony fish maintain depth and stability in water. The caudal fin aids propulsion, and the dorsal fin provides stability.
19. Million's reagent is used to test for
Solution: Million's reagent detects proteins by producing a red precipitate when heated with proteins.
20. In an (n-p-n) transistor, the (n)-type collector is connected to the positive terminal of the battery thus making the
Solution: In an (n-p-n) transistor, the base-collector junction is reverse biased to allow current amplification, while the base-emitter junction is forward biased.
21. Which type of vegetation favours both wet and hot environmental conditions?
Solution: Tropical forests thrive in hot and wet conditions, unlike savannahs or mangroves, which have specific environmental adaptations.
22. During drought, some plants dry out because of high
I. atmospheric temperature
II. humidity
III. rate of evaporation
Solution: High atmospheric temperature and evaporation rate cause plants to lose water during drought. High humidity would reduce water loss.
23. Soil erosion on sloppy farmlands is best controlled by
Solution: Terracing is the most effective method for controlling soil erosion on slopes by reducing water runoff and stabilizing soil.
24. A viable seed is one that
Solution: A viable seed can germinate under suitable conditions, indicating it is alive and capable of growth.
25. Which of the following pairs of structures form part of the female reproductive system of humans?
Solution: The cervix and uterus are parts of the female reproductive system. The urethra and ureter are part of the urinary system.
26. Which of the following chemical symbols is that of a metal?
Solution: Ca (calcium) is a metal. Ne (neon) is a noble gas, and P (phosphorus) and S (sulfur) are nonmetals.
27. All the living and non-living things that surround an organism constitute its
Solution: The environment includes all living and nonliving things surrounding an organism. Habitat is the specific place where it lives, and an ecosystem includes interactions.
28. Which of the following crops should be planted after cassava in crop rotation?
Solution: Cowpea, a legume, is ideal in crop rotation after cassava as it fixes nitrogen, improving soil fertility.
29. Endoparasites in farm animals can be controlled by
Solution: Drenching involves administering oral medication to control endoparasites (internal parasites) in farm animals.
30. Which of the following devices requires the use of transistors in its operation?
Solution: Computers rely on transistors for processing and amplification in their circuits. The other devices do not primarily use transistors.
31. Feel Method is used to determine soil
Solution: The feel method assesses soil texture by evaluating its particle size and consistency when rubbed.
32. Which of the following modes of heat transfer is the thermos flask designed to minimize?
Solution: A thermos flask minimizes conduction (via insulation), convection (via vacuum), and radiation (via reflective surfaces) to maintain temperature.
33. An atom of an element is represented as \(\frac{25}{12} X\). What is the respective number of neutrons and protons in the atom?
I. Conduction
II. Convection
III. Radiation
Solution: The notation \(\frac{25}{12} X\) indicates a mass number of 25 (protons + neutrons) and atomic number of 12 (protons). Neutrons = (25 - 12 = 13), so the answer is 13 neutrons and 12 protons.
34. The anemometer is an instrument used in determining
Solution: An anemometer measures wind speed, not rainfall, humidity, or light intensity.
35. Which of the following subjects is/are considered as applied science?
I. Biology
II. Medicine
III. Psychology
Solution: Medicine and psychology are applied sciences, using scientific principles for practical applications. Biology is a basic science.
36. Chinchilla is a breed of
Solution: Chinchilla is a breed of rabbits, often raised for fur or as pets.
37. Which of the following characters is not acquired through heredity?
Solution: Language spoken is learned, not inherited. The other traits have a genetic basis.
38. The food nutrient which ensures good health in farm animals is
Solution: Vitamins are essential for overall health, supporting various physiological functions in farm animals.
39. The use of resistant breeds of farm animals to control pests is a
Solution: Using resistant breeds is a biological pest control method, leveraging natural traits to reduce pest impact.
40. Which of the following arrangements show the correct order of increasing complexity of structures in living organisms?
Solution: The correct order of complexity is cells (basic units), tissues (groups of similar cells), organs (combinations of tissues), and systems (groups of organs working together).
1. Question 1
(a) In an experiment to demonstrate a property of light, three cardboards, \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\) with holes in their centres are arranged in a straight line between a lighted bulb and an observer as shown in the illustration below.
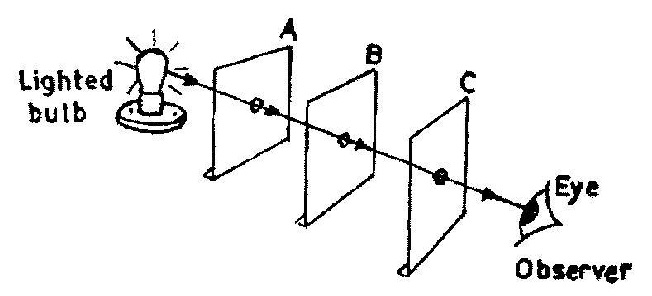
(i) What would the observer see from the position shown?
(ii) What would the observer see when cardboard \(\mathbf{B}\) is slightly displaced from the line?
(iii) Explain the observation made in (a)(ii) above.
(iv) What would be observed when the cardboard \(\mathbf{B}\) is brought back to its original position?(v) What property of light is being demonstrated in this experiment?
(vi)((\alpha)) Mention two natural occurrences that could be explained by the property of light demonstrated.\((\beta)\) Mention one device that works on the property of light demonstrated.
(b) The diagrams below are illustrations of hazard symbols found in everyday life.
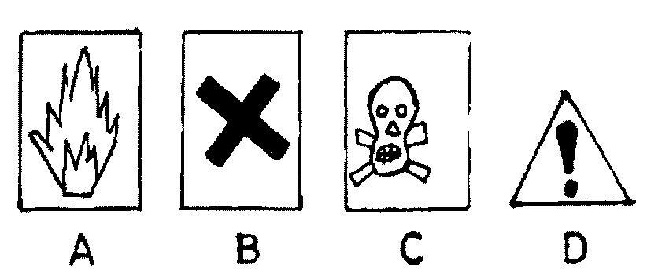
(i) What does each symbol \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}, \mathbf{C}\) and \(\mathbf{D}\) represent?
(ii) Name one substance each that is associated with each of the symbols \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\).
(iii) Name one place where the symbol \(\mathbf{D}\) can be found.(iv) State two advantages of hazard symbols.
(c) The diagrams below are illustrations of the different types of teeth in humans.
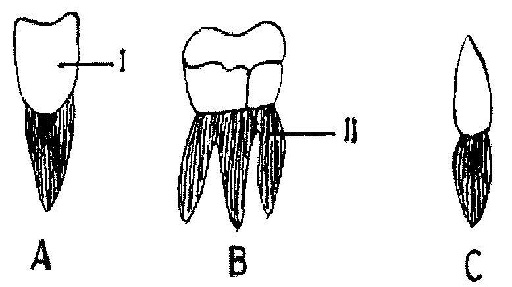
(i) Identify each type of teeth labeled \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\).
(ii) Describe the shape of each of the teeth labeled \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\).
(iii) State one function of each of the teeth labeled \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}\) and \(\mathbf{C}\).
(iv) Name the parts of the teeth labeled \(\mathbf{I}\) and \(\mathbf{II}\).
(d) The diagrams below are illustrations of some farm tools.
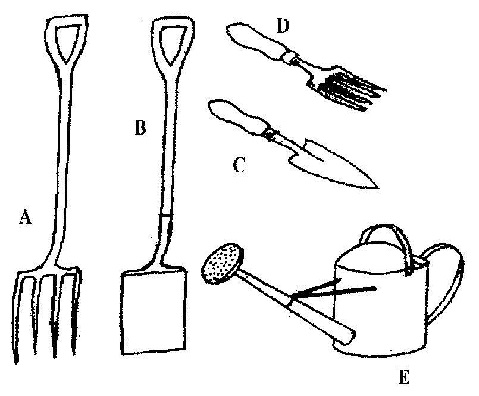
(i) Identify each of the tools labeled \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}, \mathbf{C}, \mathbf{D}\) and \(\mathbf{E}\).(ii) Mention one use of each of the tools labeled \(\mathbf{A}, \mathbf{B}, \mathbf{C}, \mathbf{D}\) and \(\mathbf{E}\).
Solutions for Question 1
(a)(i) Light rays from the lighted bulb.
(ii) Sees no light or a portion of cardboard \(\mathbf{B}\).
(iii) Since light moves in a straight line, the observer sees the light only when the holes are in a straight line with the light source. Since light rays cannot bend around the cardboard (\mathbf{B}) when slightly displaced, the observer does not see the light.(iv) The observer would see the light rays from the lighted bulb again.
(v) The property that light travels in a straight line or rectilinear propagation of light.
(vi) \((\alpha)\)
Eclipse of the sun (solar eclipse)
Eclipse of the moon (lunar eclipse)
Day and night
Shadow \((\beta)\)
Camera
Microscope
Telescope
Binoculars
Periscope
Torch
(b)(i) \(\mathbf{A}\): Highly inflammable or flammable
\(\mathbf{B}\): Irritant or can cause harm
\(\mathbf{C}\): Poisonous or toxic or deadly
\(\mathbf{D}\): Danger ahead(ii)
\(\mathbf{A}\): Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), petrol, kerosene, spirit, ethanol
\(\mathbf{B}\): Concentrated hydrochloric acid \((\ce{HCl})\), concentrated sulphuric acid \((\ce{H2SO4})\), concentrated magnesium hydroxide \((\ce{Mg(OH)2})\), concentrated sodium hydroxide \((\ce{NaOH})\)
\(\mathbf{C}\): Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) \((\ce{C14H9Cl5})\), potassium cyanide \((\ce{KCN})\), sodium cyanide \((\ce{NaCN})\), mercury(iii) On roads, at construction sites, very high voltage plants/devices(iv)
They help prevent accidents by making people take precautions.
They serve as warnings to prevent injuries or death.
(c)(i) \(\mathbf{A}\): Incisor
\(\mathbf{B}\): Premolar / molar
\(\mathbf{C}\): Canine(ii)
\(\mathbf{A}\): Chisel shaped
\(\mathbf{B}\): Almost flat surface with small projections / cusps / ridges
\(\mathbf{C}\): Pointed(iii)
\(\mathbf{A}\): Biting or cutting
\(\mathbf{B}\): Chewing or grinding or mashing
\(\mathbf{C}\): Tearing(iv)
\(\mathbf{I}\): Enamel/crown
\(\mathbf{II}\): Root
(d)(i) \(\mathbf{A}\): Garden fork
\(\mathbf{B}\): Spade
\(\mathbf{C}\): Hand trowel
\(\mathbf{D}\): Hand fork
\(\mathbf{E}\): Watering can
(ii) \(\mathbf{A}\): Breaking up soil or making soil loose or ploughing soil or turning over soil
\(\mathbf{B}\): Collecting soil or mixing substance such as animal feed or digging ground or making surface of ground level
\(\mathbf{C}\): Earthing up crops or transplanting seedlings or spreading fertilizer or manuring or mounding certain crops
\(\mathbf{D}\): Breaking up soil or making soil loose or ploughing soil or turning over soil
\(\mathbf{E}\): Watering soil / crops
2. Question 2
(a)(i) What are ruminants?
(ii) Give two examples of ruminants.
(b)(i) What is force?
(ii) State two effects of forces on a body.
(c)(i) Mention two ways in which the carbon cycle can be maintained.
(ii) State one environmental effect when the carbon cycle is disrupted.
(d)(i) Mention the three sub-atomic particles.
(ii) State the relative charge on each of the three sub-atomic particles mentioned in (d)(i) above.
(iii) Name the particle formed when an atom loses an electron.
Solutions for Question 2
(a)(i) Ruminants are cud-chewing hoofed mammals with multiple-chambered stomach.
(ii)Camel
Goat
Sheep
Giraffe
Cow
(b)(i) A force is a push or pull exerted on a body. Or: A physical influence that tends to change the position or shape of an object with mass.
(ii)
Can cause a moving body to come to rest (stop moving)
Can cause a body at rest to move
Can cause a moving body to accelerate
Can cause a moving body to decelerate
Can change the direction of a moving body
Can change the shape of a body
(c)(i)
Afforestation (planting new trees to replace the ones that have been destroyed or cut down)
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Reducing the amount of carbon dioxide emissions from industries
Avoiding excessive bush burning
Reducing the amount of fumes from vehicles
(ii) Global warming as a result of the depletion of the ozone layer
Increase in volume of sea water due to melting of icebergs
Greenhouse effect
(d)(i)
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
(ii)
Proton: Positive (+1)
Neutron: No charge or neutral (0)
Electron: Negative (-1)(iii) Cation
3. Question 3
(a)(i) What is a mixture?
(ii) Explain why some mixtures are thoroughly stirred before they are used.
(b)(i) What is reflection of light?
(ii) State two characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
(c)(i) What is a fertilizer?
(ii) Give one example of an inorganic fertilizer.
(d)(i) What is indiscriminate sex?
(ii) State two dangers of indiscriminate sex on humans.
Solutions for Question 3
(a)(i) A mixture is a physical combination of two or more substances. Or: A substance consisting of two or more substances that have been combined physically.
(ii) To attain a uniform mixture or to make it homogenous, since the original mixture may not be uniform or there may be some suspended particles of the solute.
(b)(i) Reflection of light is the bouncing back or redirection of light when it strikes a surface.
(ii)
Same size as object
Same distance from mirror as object
Virtual
Erect / upright
Laterally inverted
(c)(i) A fertilizer is any substance usually added to or spread onto soil to increase its ability to support plant growth. Or: A substance added to soil to increase its nutrient content or fertility.
(ii)
NPK
Ammonium sulphate
Urea
Potassium chloride (or muriate of potash)
(d)(i) Indiscriminate sex is having sexual intercourse with multiple (two or more) partners and usually without protection (use of condom).
(ii) Contracting sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as AIDS, syphilis, etc.
Teenage pregnancy (where teenagers are involved)
Abortion, which is usually quite dangerous to the mother
Loss of social respect / reputation
Loss of self-esteem
4. Question 4
(a)(i) What is a simple machine?
(ii) Give two examples of a simple machine.
(b)(i) What is rusting?
(ii) State two effects of rusting.
(c)(i) What are food nutrients?
(ii) Classify the following food items as carbohydrate, fats and oil or protein: Beans, palm fruits, meat, margarine, bread and maize.
(d)(i) State two effects of malnutrition in farm animals.
(ii) Mention one disease of farm animals caused by virus.
Solutions for Question 4
(a)(i) A simple machine is a mechanical device that makes work easier and/or faster.
(ii)
Bottle opener
Wheel barrow
Nut cracker
Inclined plane
Spanner
Crowbar
(b)(i) Rusting is the corrosion (wearing away) of the surface of iron or steel due to the formation of iron oxide. Or: The formation of a reddish brown coating of iron oxide on the surface of iron or steel that forms when the metal is exposed to air and moisture.
(ii)
Shortage of life span of item
Loss of beauty of item
Reduction in effectiveness of implement
Collapse of buildings
(c)(i) Food nutrients are chemical substances, found in food, that the body needs in order to function properly.
(ii)
Carbohydrate: Bread, Maize
Fats and oils: Palm fruits, Margarine
Protein: Beans, Meat
(d)(i)
Deficiency diseases
Stunted growth
Low energy and activity (lack of vitality)
Slow recovery from illnesses
Death
Lower reproduction
(ii)
Rabies
Bird flu
Newcastle
Rinder pest
5. Question 5
(a)(i) What is soil erosion?
(ii) Name two methods of controlling soil erosion.
(b)(i) Explain each of the following terms as used in ecology:((\alpha)) Adaptation((\beta)) Endangered species
(c)(i) Give one example of hard water.
(ii) Explain why it is advisable to drink water which is hard.
(d)(i) What is magnetic field?
(ii) State two methods of making magnets.
Solutions for Question 5
(a)(i) Soil erosion is the washing away of the top soil by agents of erosion. Or: The removal of soil material by natural processes, principally running water, glaciers, waves, and wind.
(ii)Planting of cover crops
Planting of grasses
Planting of wind breaks (trees)
Ploughing across slopes
Terracing
Strip cropping
(b)(i) \((\alpha)\) Adaptation: The development of physical and behavioral characteristics that allow organisms to survive and reproduce in their habitats.\((\beta)\) Endangered species: Species threatened by extinction. Or: Species whose numbers are so few, or are declining so quickly, that the animal, plant, or other organism may soon become extinct.
(c)(i)
Deep well water
Borehole water
(ii) It is advisable to drink hard water because it contains dissolved mineral salts, such as calcium and magnesium salts, which are necessary to maintain good health and proper functioning of the body. (Minerals are essential for the healthy growth of teeth and bones. They also help in cellular activities, such as enzyme action, muscle contraction, nerve reaction, and blood clotting.)
(d)(i) Magnetic field is a region of space surrounding a magnet or current-carrying circuit in which the resulting magnetic force can be detected.
(ii)
Electrical method
Single stroking
Double stroking
Induction
Hammering
6. Question 6
(a)(i) Define each of the following terms: \((\alpha)\) Solvent \((\beta)\) Solute
(ii) Name one common solvent used in the home.
(b)(i) Ration
(ii) Dehorning
(c)(i) What is an element?
(ii) Write down the symbol of each of the following chemical substances: \((\alpha)\) Potassium \((\beta)\) Sulphur
(d)(i) Mixed farming
(ii) Mixed cropping
Solutions for Question 6
(a)(i) \((\alpha)\) Solvent: A substance that dissolves things. Or: A substance in which other substances are dissolved, usually a liquid.((\beta)) Solute: A substance that is dissolved in another substance.
(ii)
Water
Turpentine
Liquid soap
Alcohol
Kerosene
(b)(i) Ration: A fixed and limited amount of feed, given to an animal or group of animals at specific times/intervals. This is done to ensure that the animal has the right amounts of essential food nutrients for healthy growth and development.
(ii) Dehorning: Removing or preventing the growth of the horns of an animal by surgery or cauterization. This is done primarily to prevent animals from using them to injure other animals or destroy property.
(c)(i) An element is a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms. Or: Any substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler one by a chemical reaction.
(ii) \((\alpha)\) Potassium: \(\ce{K}\) \((\beta)\) Sulphur: \(\ce{S}\)
(d)(i) Mixed farming: The cultivation of crops and the rearing of livestock on the same farm at the same time. Or: Farming that combines growing crops and rearing livestock on the same farm at the same time.
(ii) Mixed cropping: The cultivation of different kinds of crops on the same piece of land at the same time.